The Challenge
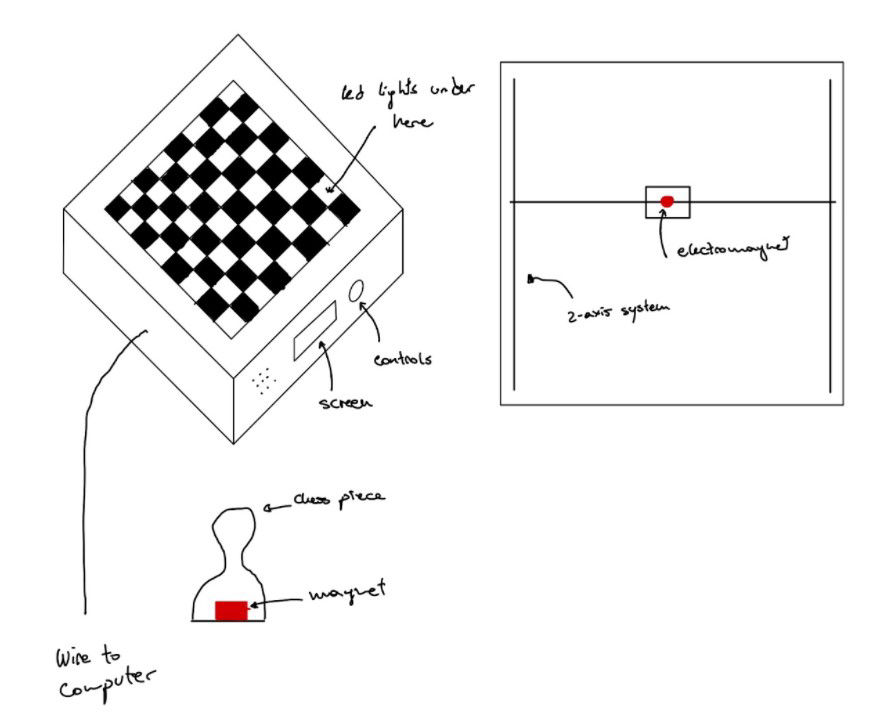
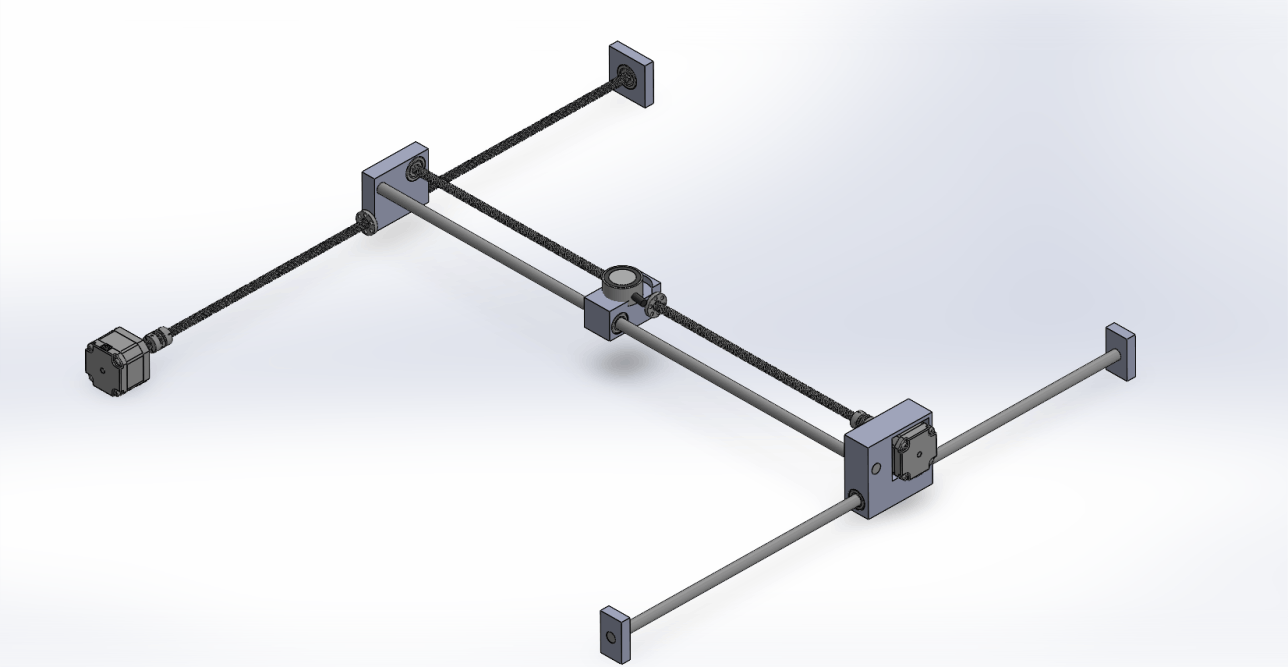
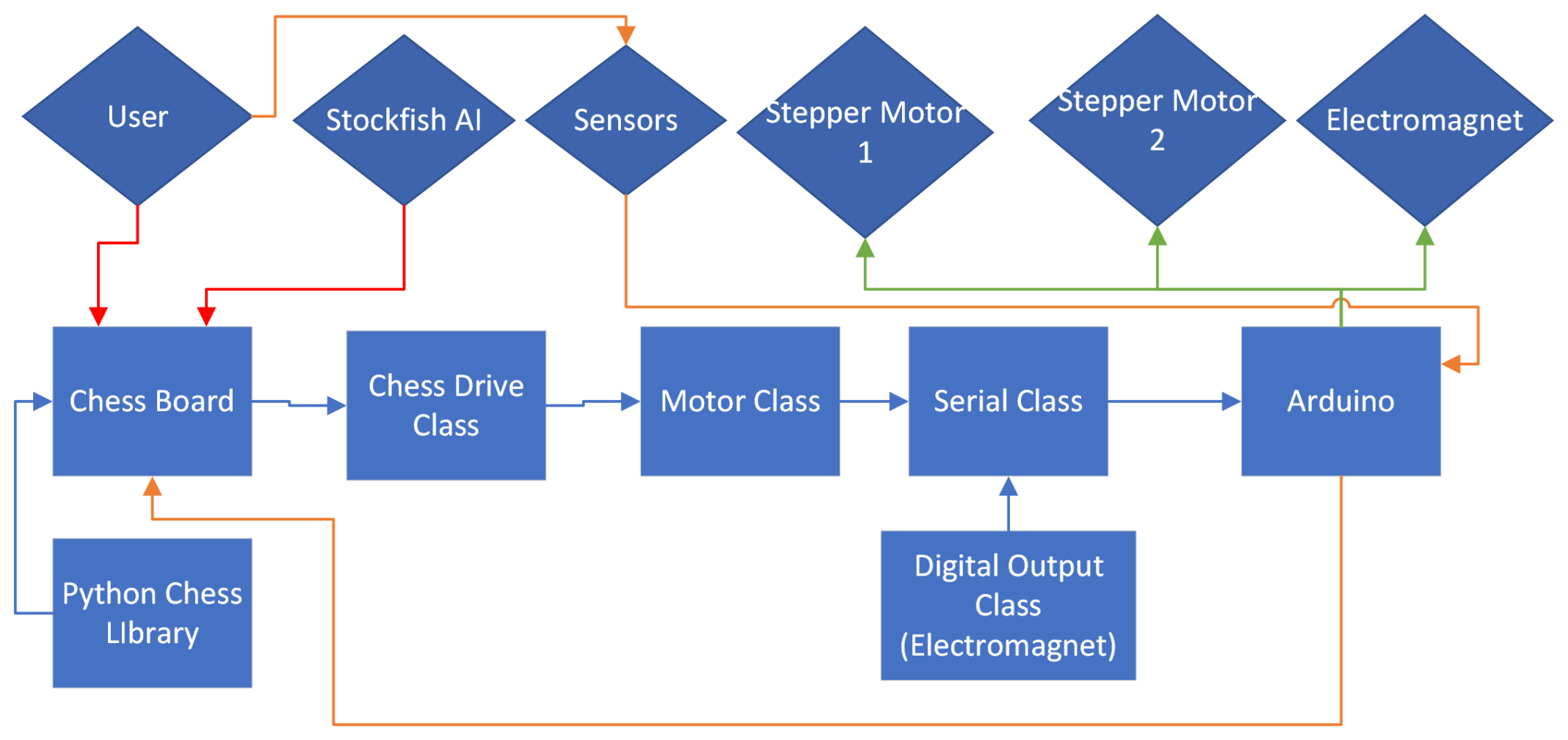
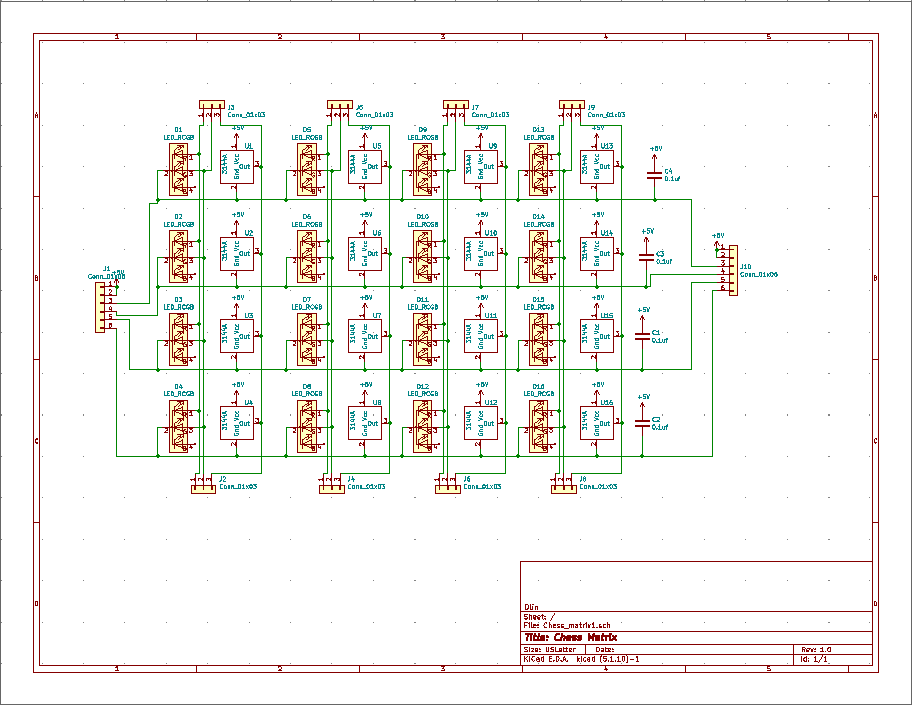
Creating an autonomous chess-playing system presented several key challenges that required innovative solutions across multiple engineering disciplines. The primary goal was to develop a mechanism that could move chess pieces without human intervention while maintaining the authentic feel of playing chess.
The system needed to reliably detect player moves, integrate a chess AI with physical movement systems, and build a robust physical structure to house all components. Most importantly, it had to create a seamless user experience that preserved the tactile and visual aspects of real-life chess playing.